
Welcome to Lulua-Dubai Company
Discover Quality, Experience Excellence

Discover Quality, Experience Excellence
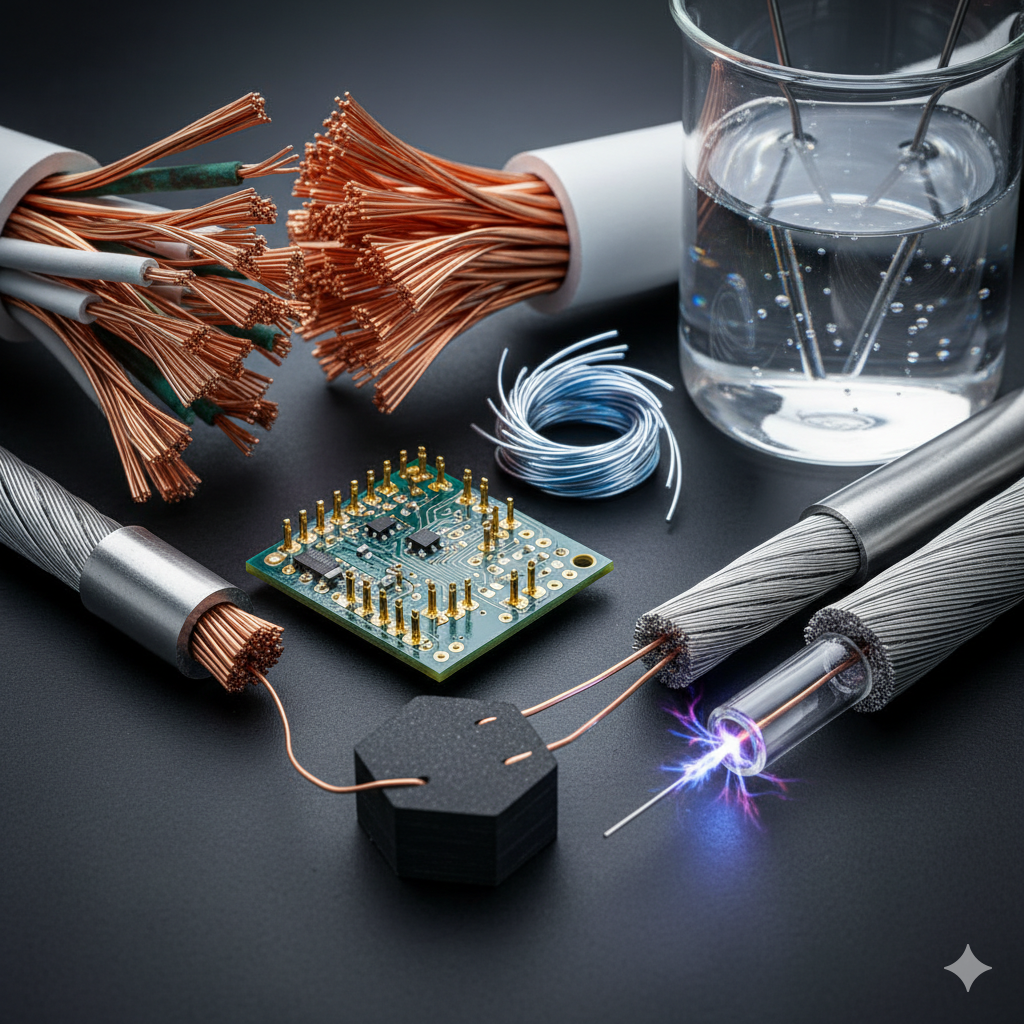
An electrical conductor is a material that allows electricity to flow through it easily. This is in contrast to an insulator, which resists the flow of electricity. The ability of a material to conduct electricity is determined by the movement of electrons within its atomic structure.
In conductive materials, the outermost electrons of the atoms, known as valence electrons, are loosely bound to their respective nuclei. These electrons are free to move between atoms, forming what is often referred to as an "electron sea." When an electrical voltage is applied across a conductor, it creates an electric field that pushes these free electrons in a particular direction, resulting in an electric current.
Key Properties of Conductors:
Low Resistance: Conductors have low electrical resistance, meaning they don't impede the flow of current significantly.
High Conductivity: This is the reciprocal of resistance, indicating a material's ability to conduct current.
Free Electrons: The presence of free or mobile electrons is the fundamental reason for their conductive properties.
Common Conductive Materials:
Metals: Most metals are excellent conductors.
Copper: Widely used in electrical wiring for homes, buildings, and power transmission due to its excellent conductivity and relatively low cost.
Silver: The best electrical conductor, but its high cost limits its use to specialized applications where superior performance is critical, such as in high-frequency connectors or scientific instruments.
Gold: Highly conductive and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for connectors, contacts, and circuit board components where reliability is paramount.
Aluminum: Lighter and cheaper than copper, often used in high-voltage transmission lines and some types of electrical wiring, especially for larger gauge applications.
Electrolytes: These are solutions containing ions that can carry an electric current. For example, salt water.
Plasma: An ionized gas containing free electrons and ions, plasma is an excellent conductor and is found in lightning, neon signs, and stars.
Graphite: A form of carbon, graphite has delocalized electrons that allow it to conduct electricity, making it useful in electrodes and brushes for electric motors.
Applications of Conductors:
Conductors are essential to virtually every aspect of modern electrical and electronic systems. They are used in:
Wiring: Powering homes, businesses, and industrial facilities.
Electronic Circuits: Connecting components within devices like computers, smartphones, and televisions.
Power Transmission: Carrying electricity from power plants to consumers over long distances.
Heating Elements: In toasters and electric heaters, where resistance is used to generate heat.
Understanding conductors is fundamental to electrical engineering and plays a crucial role in designing efficient and reliable electrical systems.